Scientific evidence of the benefits of meditation on health and wellbeing
More and more research is showing the physiological and psychological benefits of having a meditation practice.
The Mindfulness Report from 2010 explored the available research and showed meditation typed disciplines can improve both mental and physical health. The report started to combine modern science with ancient knowledge to show the benefits. The report particularly highlights the benefits of meditation in the workplace to improve productivity and decrease the incidence of sick days.
Their review of research showed that people who meditate are “less likely to experience psychological distress including depression and anxiety.” It also showed that people who meditate can have a greater awareness, acceptance and bounce back from bad moods quicker. It suggested meditators levels of focus, attention and productivity at work are greater, as well as greater levels of satisfaction, better relationships and they are less likely to act on impulse.
How does meditation create physiological change in the brain?
Research looking at the physiological changes in the brain during or after meditation practice tends to use neuroimaging. This might be in the form of:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI),
- functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). The MRI and fMRI show changes to blood flow to the brain showing higher metabolic activity.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) machines use dyes to show contrast.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG) which reveals electrical activity in the brain using electrodes attached to the scalp showing your brain waves.
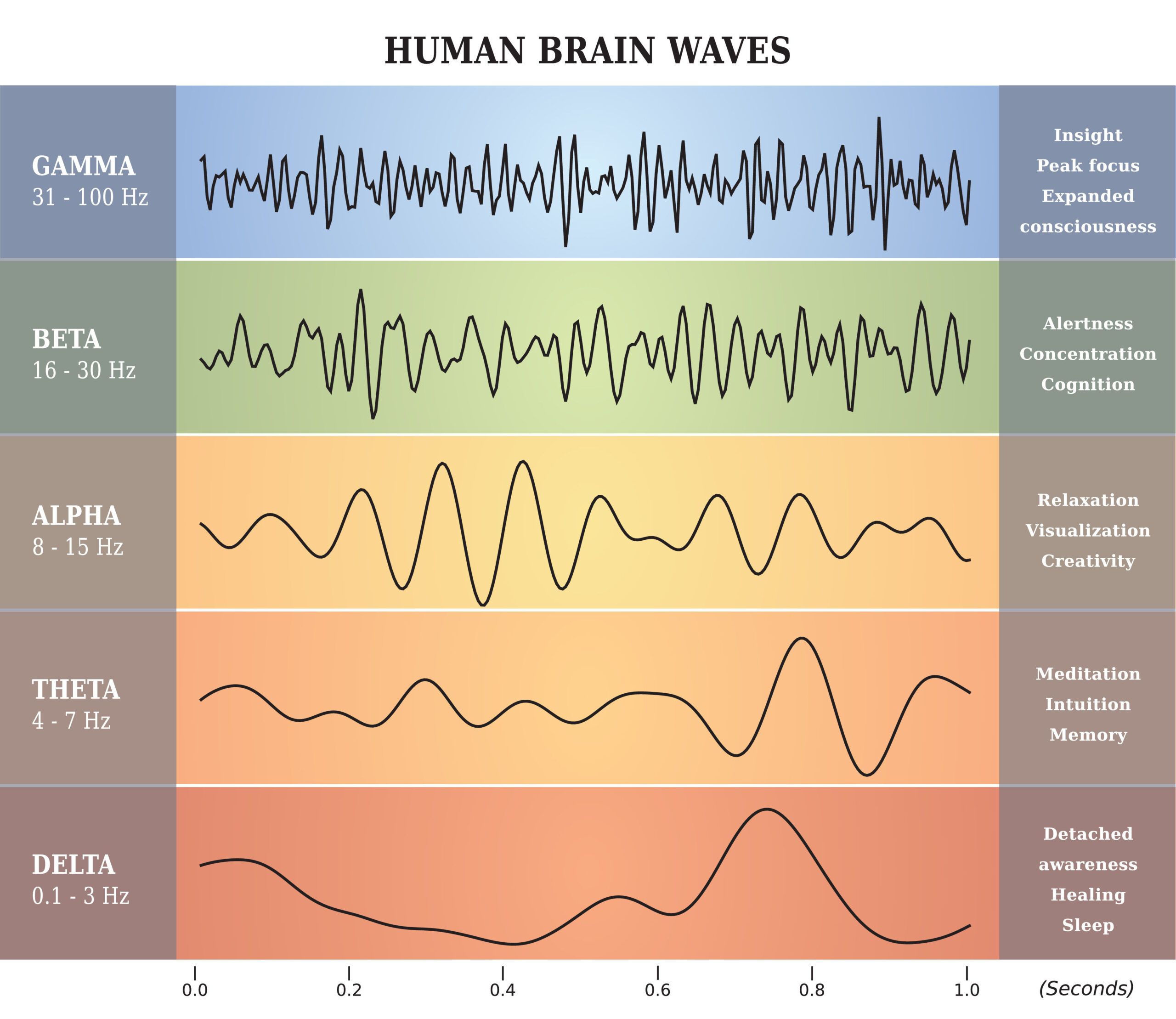
Brain waves are the oscillating electrical voltage within the brain and are detected on an EEG. Different parts of the brain have different frequencies and how you feel will change depending on the frequency your brain is functioning at and create homeostasis. The five main waves looked at are GAMMA, BETA, ALPHA, THETA, DELTA (shown in the image above).
- Gamma (30-100Hz) occurs when we are problem solving, focused and concentrating.
- Beta (12-30Hz) is our common existence when we are awake, alert, busy mind and conscious.
- Alpha (8-12Hz) is restful, reflective, relaxed and calm without thoughts.
- Theta (4-7Hz) is deep relaxation or meditation, possible with drowsiness or mental imagery.
- Delta (up to 4Hz) occurs when we are in a deep, dreamless sleep.
How the brain waves are altered by meditation
Research by Travis et al, shows that meditation slows down brain activity and the peaks of waves reduce. We might experience this in a positive way as a reduced mental chatter, anxiety and worry which helps with decision making and mental clarity. During the meditation practice the brain waves change from alertness to calm and silence and returns to alertness.
Boccia’s review on meditation with fMRI shows an increase in activation in areas of the brain linked with attention, mind wandering, recovery of sporadic memories and emotional processing whilst meditating. Particularly within the “prefrontal cortex, parietal areas, middle cingulate cortex, hippocampal and parahippocampal formations.”
For people new to meditation prior to starting meditation their brain waves are often functioning at BETA wave levels. When they start to meditate their brain waves flip into ALPHA. This means their brains waves become less frenetic in shape and speed. The aim is not to fall asleep in most meditations however if the meditator falls asleep when they meditate their brain will flip into DELTA mode. Personally and lots of people have mentioned to me, I often find during meditation find the answers I have been looking for come to mind. This is often because we have shifted our perception, we are changing our brain waves and maybe alternating between GAMMA, ALPHA and THETA waves.
Sound Therapy is very powerful at changing brain waves; as soon as you hear the sounds, your brain waves switches to alpha or maybe even deeper brain waves. This is why Sound Therapy is particularly good if you struggle with meditation as it helps you to relax deeper and switch brain waves quickly. This particularly helps people who struggle to calm or switch off their minds.
How does meditation affect the body with physiological changes?
Bruce Barrett’s research suggests that meditation reduces the duration of illnesses, thus improving immunity, however they suggest more research is needed. The Mindfulness Report supports this by saying meditation improves the functioning of the immune system and people have fewer hospital admissions. It also highlights that meditation increases blood flow, reduces blood pressure and reduces risk of hypertension.
Meditation also activates the parasympathetic nervous system and the vagus nerve. This increases the vagal tone and inhibits cytokine production. This is important as the brain and gut are deeply connected and can influence feelings of depression, anxiety and mood. Research by Breit suggests the correlation between vagal tone and the capacity to regulate stress responses which can help with resilience and improvement in mood and anxiety.
The Mindfulness Report also shows that meditation increases blood flow, reduces blood pressure and reduces the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, meditators have a lower number of hospital admissions for heart disease, cancer, infectious disease alongside ½ the visits to their GP, compared with those who don’t meditate.
Research by Benson has shown that meditation can activate the relaxation response, which is an intrinsic mechanism to reduce the effects of stress on the body. The mechanism that switches off the flight, flight, freeze and façade mechanism. Through focusing on breathing it is possible to “decrease heart rate, lower metabolism, decrease rate of breathing, and in this way bringing the body back into a healthier balance.” This helps to reduce the rate of cellular decay and so slows down the rate of aging. Research by Melville has also shown that 15 minutes of meditation in the office can activate the relaxation response.
Meditation has been shown to improve sleep quality and quantity too. A review by Nagendra showed that practiced meditators spend more time in theta-alpha brain waves with background delta waves. As well as reduced brain activity and enhanced Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, this is because Meditation helps to increase melatonin levels which improve the quality of sleep.
How does meditation affect the body with psychological changes?
Dr Travis also shows that regular meditation increases activity of the left prefrontal cortex in the brain, which ultimately helps people feel happier. Dr David Hamilton also discussed how regular meditation over a period of time increases neural connections within the front of the brain (neural wiring) and specifically compassion meditation (loving kindness) creates more activity in the left frontal cortex which is where empathy is created.
The review by Boccia further supports this by saying that meditation activates parts of the brain involved with processing self-relevant information, self regulation, focused problem-solving, adaptive behaviour, and interception.
The Mindfulness Report suggests that regular meditation increases the size of the parts of the brain such as the hippocampus, oribito-frontal cortex, thalamus and inferior temporal lobe which are used for emotion regulation.
Research by Holzel and Sara Lazar used MRI scans to show repeated meditation creates changes in the brain called neuroplasticity where the amount of grey matter increases. As we age the frontal cortex shrinks, which is why people often struggle with memory issues, but through meditation this can be limited. Meditation also increases the size of the hippocampus which helps with learning, memory and regulation of emotions. The right basal amygdala grey matter decreases whilst perceived stress levels decrease. Therefore, meditation helps to decrease stress levels, improves memory, helps people to process emotions better and slows down the aging process.
The Mindfulness Report has also shown that people who meditate are more in control of their behaviour and change their internal thoughts and reactions. Discussing the reduction of stress levels, better mood regulation and less anxiety alongside a reduction in aggressive behaviour and switch to tolerance and compassion. Mindfulness also increases the awareness people have about themselves and can improve vitality. It also highlights a reduction of addictive behaviour, for example to illegal drugs, prescribed medications, as well as the consumption of alcohol and caffeine.
A really interesting subject area to me is the research into the effects of meditation on those suffering from chronic pain in The Mindfulness Report. It shows research where people in chronic pain (a protective mechanism from the brain if nothing structurally wrong) who also mediated had less pain, their lives were less restricted by pain and furthermore less medication was required to manage their symptoms. Amazingly, this lasted until at least the 15 month follow up review.

Summary of the benefits of meditation
Physiological benefits of meditation
- helps reduces stress, blood pressure & heart rate
- helps you sleep better & wake up feeling more refreshed
- reduces cortisol & adrenaline levels
- can help with menopause and thyroid symptoms
- improves lung capacity and reduces breathing rate
- reduces cholesterol & can help people to lose weight
- improve pain tolerance
- improves energy levels, concentration & memory
- positive changes to skin & hair health
- boosts immunity

Physiological benefits of meditation
- reduces feelings of anxiety and stress
- creates coping mechanisms & a greater capacity to deal with situations
- reduces depression
- helps you feel connections to people
- reduces feelings of anger or frustration
- awakens a greater awareness which allows you to catch issues earlier
- you may be more open minded to change
- creates space and clarity between thoughts
- more self aware & compassionate
- problem solving ability improves and productivity increases
- creates a feeling of love, calm & happiness
- and can help you deal with difficult emotions

Spiritual benefits of meditation
- a sense of connection
- a deeper understanding whether that’s to self, to others or nature
- helps to bring emotions to the surface
- raises your vibration
- happiness
- can develop a sense of higher purpose
- inner wisdom
- and can connect you to religion in a deep way if you are religious
- realisation that each person experiences connections differently
Bibliography
- Barrett et al, 2018 Meditation or exercise for preventing acute respiratory infection (MEPARI-2): A randomized controlled trial.
- Benson the relaxation response https://www.brighamandwomensfaulkner.org/assets/faulkner/headache-center/documents/relaxation-response.pdf.
- Boccia et al, 2015 The Meditative Mind: A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of MRI Studies.
- Breit et al, 2018 Vagus Nerve as Modulator of the Brain–Gut Axis in Psychiatric and Inflammatory Disorders.
- BSOM Manual.
- David Hamilton Meditation: Scientific Evidence of it’s Effect. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iOiizr2FvAw
- Holzel and Sara Lazar, 2010 Stress reduction correlates with structural changes in the amygdala.
- Lazar, How Meditation Can Reshape Our Brains: Sara Lazar at TEDxCambridge 2011 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m8rRzTtP7Tc.
- Melville et al, 2012 -Fifteen Minutes of Chair-Based Yoga Postures or Guided Meditation Performed in the Office Can Elicit a Relaxation Response.
- Mindfulness report 2010.
- Nagendra,2012 Meditation and its regulatory role on sleep.
- Priyanka et al, Technological Basics of EEG Recording and Operation of Apparatus.
- Travis et al, 2009 Effects of Transcendental Meditation practice on brain functioning and stress reactivity in college students.
- Travis Introduction to EEG- and Speech-Based Emotion Recognition, 2016
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ddKlPAxVITk.
Claim Your special offer ‘mindfulness meditation beginners online or in person session’ or book a relaxing soundbath
To claim yours now, simply click on the orange button below and then chose the option that suites you best on the next page
